Can what you eat really affect how you feel?
For years, mental health and nutrition were studied as two separate fields. But today, researchers in the what you put on your plate shapes your brain, mood, and overall wellbeing.
From the gut–brain connection to the role of vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, science now shows that nutrition and mental health are deeply linked. A poor diet can worsen anxiety, depression, and stress, while a balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help you feel calmer, more focused, and emotionally resilient.
This complete guide will walk you through:
- The science behind nutrition and mental health.
- Foods that boost mood and protect the brain.
- Foods that may harm your mental wellbeing.
- Eating patterns and practical tips for daily life.
By the end, you’ll have actionable steps to eat for your mind as much as your body—helping you create a lifestyle that supports both health and happiness
The Science Linking Nutrition and Mental Health

The connection between nutrition and mental health is no longer just theory—it’s backed by neuroscience, psychology, and nutrition science. Here are the key mechanisms:
1. Brain Chemistry and Neurotransmitters
Your brain needs raw materials (nutrients) to create neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which regulate mood, focus, and stress.
- Amino acids from protein-rich foods → dopamine, serotonin.
- B vitamins → essential for nerve function and energy.
- Omega-3 fatty acids → support brain structure and emotional balance.
2. The Gut–Brain Axis
Over 90% of serotonin—the “happy chemical”—is produced in the gut. A healthy gut microbiome (thanks to fiber and probiotics) sends positive signals to the brain. An unhealthy gut can trigger inflammation, anxiety, and depression.
3. Blood Sugar Balance
Unstable blood sugar = mood swings, irritability, fatigue. Diets high in refined carbs and sugar spike insulin, leaving the brain exhausted. Balanced meals keep mental energy steady.
4. Inflammation and Mental Health
Chronic inflammation from processed foods is linked to depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Anti-inflammatory foods like berries, nuts, and leafy greens protect mental wellbeing.
Common Mental Health Issues Affected by Nutrition

Depression and Diet
Research shows diets rich in vegetables, whole grains, and fish lower the risk of depression. Meanwhile, highly processed foods increase depressive symptoms.
Anxiety and Food
Caffeine, sugar, and alcohol can worsen anxiety, while magnesium-rich foods (pumpkin seeds, spinach) and omega-3s can reduce it.
Stress and Nutritional Deficiencies
Stress depletes the body of B vitamins, magnesium, and vitamin C, making it harder to cope. Eating nutrient-dense foods restores resilience.
Sleep and Food Connection
Poor sleep worsens mental health. Tryptophan-rich foods (turkey, oats, bananas) and herbal teas can improve sleep quality.
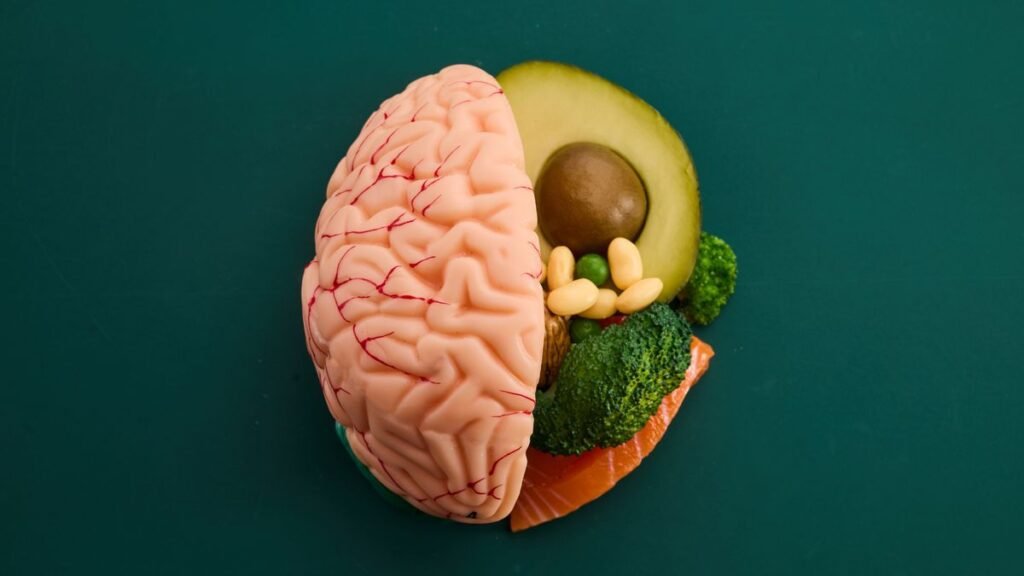
Foods That Boost Mental Wellbeing
Omega-3 Rich Foods
- Salmon, sardines, walnuts, chia seeds.
- Support memory, reduce depression symptoms.
Antioxidant Foods
- Blueberries, spinach, kale, dark chocolate.
- Fight oxidative stress linked to mood disorders.
Whole Grains & Complex Carbs
- Brown rice, oats, quinoa.
- Stabilize blood sugar, provide steady energy.
Probiotic and Fermented Foods
- Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut.
- Improve gut health and serotonin production.
Hydration
Even mild dehydration can cause brain fog, fatigue, and irritability. Aim for 8+ cups of water daily.
Foods That Harm Mental Health
- Processed foods → increase inflammation, worsen depression.
- Refined sugar → mood crashes, addictive cycles.
- Trans fats → linked to cognitive decline.
- Excess caffeine → triggers anxiety, disrupts sleep.
- Alcohol → depressant effect, poor sleep quality.
Eating Patterns That Support Wellbeing

Mediterranean Diet
Rich in vegetables, fish, olive oil, and nuts. Shown to reduce depression risk.
Mindful Eating
Focusing on food without distraction reduces stress and prevents overeating.
Balanced Meals
Each plate should include protein, fiber, and healthy fat to stabilize energy.
💡 Practical Tips to Improve Nutrition for Mental Health
- Plan weekly meals with mood-boosting foods.
- Swap soda for sparkling water or herbal tea.
- Choose whole foods over processed snacks.
- Cook at home more often—control ingredients.
- Start small: add one extra fruit or veggie per day.
👩⚕️ When to Seek Professional Support
Nutrition is powerful, but it’s not a replacement for therapy or medication. If you’re struggling with depression, anxiety, or severe stress:
- Consult a mental health professional.
- Work with a registered dietitian specializing in mental health.
- Combine therapy, nutrition, and lifestyle changes for best results.
Conclusion
Food is more than fuel—it’s information for your brain and body. By choosing a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods, you can support emotional balance, reduce stress, and even prevent mental health struggles.
Start today: add more brain foods like salmon, berries, and leafy greens to your meals. Over time, these small choices can transform both your mental and physical wellbeing.
For more, see Harvard Health’s guide on food and mood.
Want more science-backed mental health tips?
👉 Subscribe to LivingWisdomNow for weekly articles on wellbeing, productivity, and emotional resilience.
FAQ
Q: Can food really improve mental health?
Yes—nutrients directly affect brain chemistry and mood regulation.
Q: What foods are best for depression?
Omega-3 rich fish, whole grains, leafy greens, berries, and fermented foods.
Q: How does gut health affect mood?
The gut produces serotonin and communicates with the brain via the gut–brain axis.
Q: What diet reduces anxiety?
Diets high in magnesium, omega-3s, and antioxidants while avoiding sugar and caffeine.
Q: Can nutrition replace therapy or medication?
No, but it’s a powerful complementary tool alongside professional treatment.






[…] Mental health disorders refer to a range of psychological conditions that affect a person’s thinking, mood, behavior, and overall functioning. These disorders can be short-term, chronic, mild, or severe, impacting every aspect of a person’s life. The complexity of mental health makes recognizing the signs challenging, but understanding them is essential for seeking timely help. […]